Unveiling the Secrets of Tooth Decay
Dental health is a crucial aspect of our overall well-being, and one common concern many individuals face is the formation of cavities. Understanding what a cavity looks like is key to early detection and effective treatment. Let’s delve into the intricate details of cavities, exploring their appearance, causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies.
Cavities, also known as dental caries or tooth decay, are areas of the tooth that have been permanently damaged. Recognizing the signs of cavities early is vital for preventing further deterioration and maintaining optimal oral health.
Demystifying the Cavity: A Look at the Signs of Tooth Decay
A cavity, also referred to as dental caries, is a breakdown of the tooth’s hard outer layer (enamel) due to the presence of bacteria and acid. This breakdown manifests as visible damage to the tooth, causing discomfort and posing a threat to oral health.
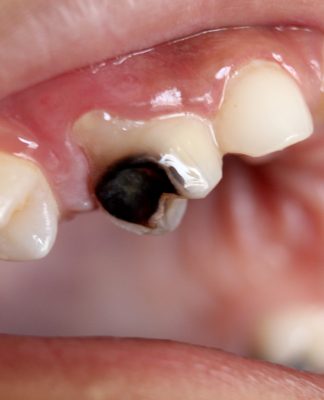
Here’s a breakdown of what a cavity might look like:
Early Stage:
- Tiny, white or light-brown spots: These are the first signs of demineralization, where the tooth’s minerals are being depleted by acid from plaque. They are often smooth and barely noticeable.
- Chalky patches: These rougher areas are a further development of demineralization, indicating the enamel’s surface is starting to weaken. Their appearance might resemble a white scratch or a slight discoloration.
Progressive Stage:
- Darker spots: As the decay progresses, the enamel breaks down further, exposing the dentin layer beneath. This dentin layer is more porous and yellowish, leading to darker spots on the tooth’s surface.
- Visible holes or pits: Once the dentin layer is compromised, the cavity can rapidly deepen, creating noticeable holes or pits in the tooth. These holes can range in size and shape, depending on the severity of the decay.
Advanced Stage:
- Stains: With significant decay, the cavity can become stained brown or black due to food particles and bacteria accumulating in the exposed dentin.
- Pain and sensitivity: In advanced stages, the cavity can reach the tooth’s pulp, causing pain and sensitivity to hot, cold, and sweet foods and beverages.
Remember: These are just generalized descriptions. The specific appearance of a cavity can vary depending on its location, size, and stage of development. If you suspect a cavity, it’s crucial to schedule an appointment with your dentist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Tooth Structure
To comprehend what a cavity looks like, it’s essential to first understand the basic structure of a tooth. Teeth consist of three layers: enamel, dentin, and pulp. Enamel, the outermost layer, plays a crucial role in protecting the tooth from decay.
Causes of Cavities
Several factors contribute to the development of cavities. Poor oral hygiene, excessive sugar and acid consumption, and the accumulation of bacteria and plaque on the teeth are common culprits.
- Poor oral hygiene
- Sugar and acid consumption
- Bacteria and plaque buildup
Symptoms of Cavities
Recognizing the symptoms of cavities is crucial for early intervention. These may include tooth sensitivity, pain while chewing, and visible holes or pits in the affected teeth.
- Tooth sensitivity
- Pain while chewing
- Visible holes or pits
The Stages of Cavity Development
Cavity formation is a gradual process involving stages such as initial demineralization, enamel decay, dentin involvement, and potential damage to the pulp inside the tooth.
- Initial demineralization
- Enamel decay
- Dentin involvement
- Pulp damage
How Cavities Are Diagnosed
Dentists employ various techniques, including dental examinations and X-rays, to diagnose cavities accurately.
- Dental examinations
- X-rays and imaging techniques
- Preventing Cavities
Preventing Cavities
Prevention is the best strategy against cavities. Regular brushing and flossing, routine dental check-ups, and a balanced diet with reduced sugar intake are effective preventive measures.
- Regular brushing and flossing
- Dental check-ups and cleanings
- Balanced diet and reduced sugar intake
Treatment Options for Cavities
If a cavity is detected, prompt treatment is essential. Dental fillings, crowns, and, in severe cases, root canals may be recommended.
- Dental fillings
- Crowns and root canals
- Importance of early intervention
Natural Remedies for Cavities
Some individuals explore natural remedies, such as oil pulling, xylitol use, and fluoride applications, to support cavity prevention.
- Oil pulling
- Xylitol use
- Fluoride applications
Cavity Myths Debunked
Dispelling common myths, like the belief that only children get cavities or that sugar-free products are cavity-free, is crucial for accurate dental care.
- Only kids get cavities
- Sugar-free means cavity-free
- Cavities heal on their own
Cavity Prevention in Children
Children are not exempt from cavities. Pediatric dental care, including sealants and fluoride treatments, is crucial for their oral health.
- Importance of pediatric dental care
Sealants and fluoride treatments
The Connection Between Diet and Oral Health
Nutrition plays a significant role in maintaining healthy teeth. Certain foods contribute to dental health, while others may increase the risk of cavities.
- Impact of nutrition on tooth health
- Foods that promote dental health
Cavities and Systemic Health
Research indicates a connection between oral health and overall well-being, emphasizing the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene practices.
-
- Link between oral health and overall well-being
- The role of inflammation
Common Mistakes in Oral Care
Incorrect brushing techniques and neglecting regular dental check-ups are common mistakes that can compromise oral health.
- Incorrect brushing techniques
- Neglecting regular dental check-ups
Conclusion
Understanding what a cavity looks like is fundamental for proactive oral care. By recognizing the signs, implementing preventive measures, and seeking prompt treatment, individuals can safeguard their dental health and enjoy a confident smile.